Bacteria:
One of two prokaryotic (no nucleus) domains, the other being the ARCHAEA. Bacteria are microscopic, simple, single-cell organisms. Some bacteria are harmless or, often, are beneficial to human beings. Others are pathogenic, causing disease and evendeath. All play a major role in the cycling of nutrients in ecosystems via AEROBIC and ANAEROBIC decomposition (saprophytic). Some species form symbiotic relationships with other organisms, such as legumes, and help them survive in the environment by fixing atmospheric nitrogen. Many different species exist as single
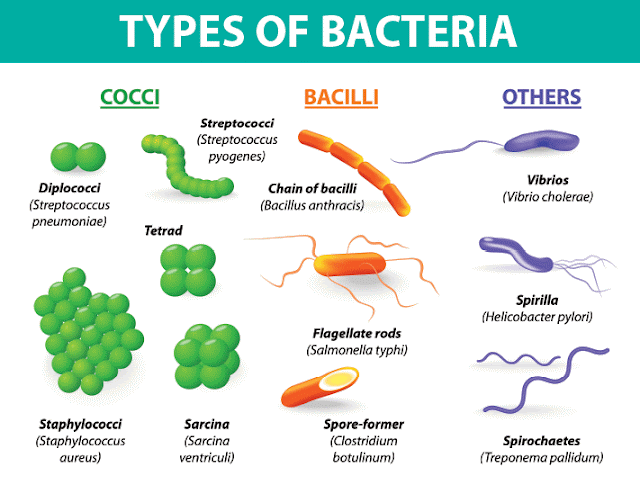
cells or colonies, and they fall into four shapes based on the shape of their rigid cell wall: coccal (spherical), bacillary (rod-shaped), spirochetal (spiral/helical or corkscrew), and vibro (comma-shaped). Bacteria are also classified on the basis of oxygen requirement (aerobic vs. anaerobic).
No comments:
Post a Comment